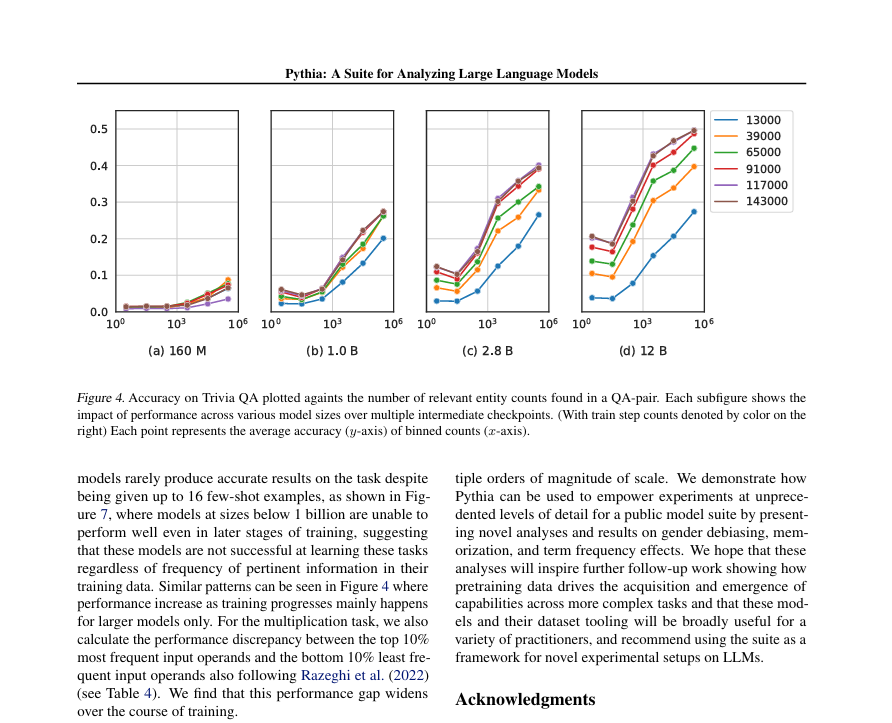
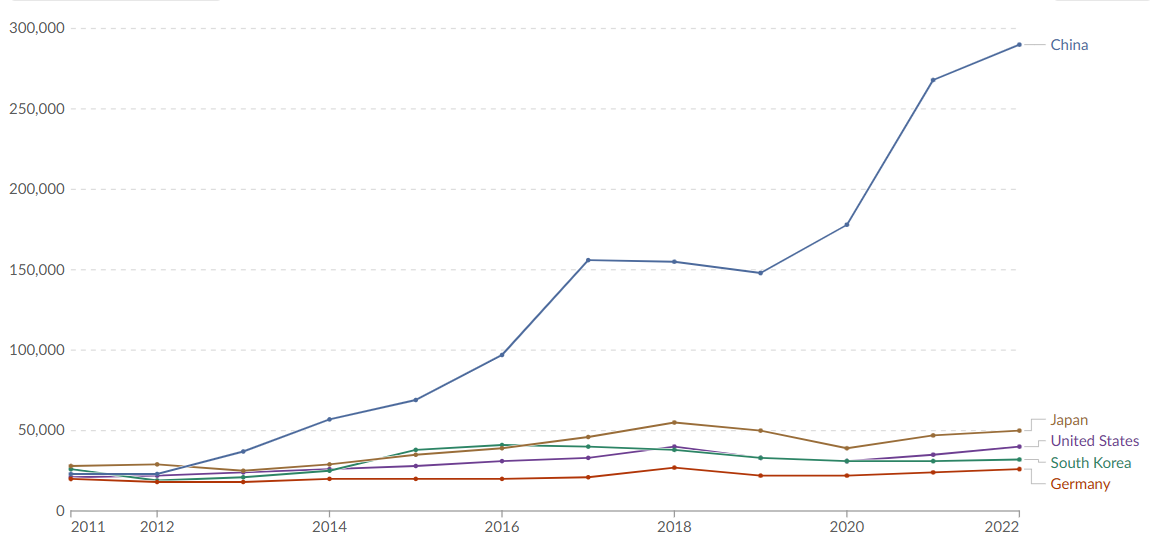
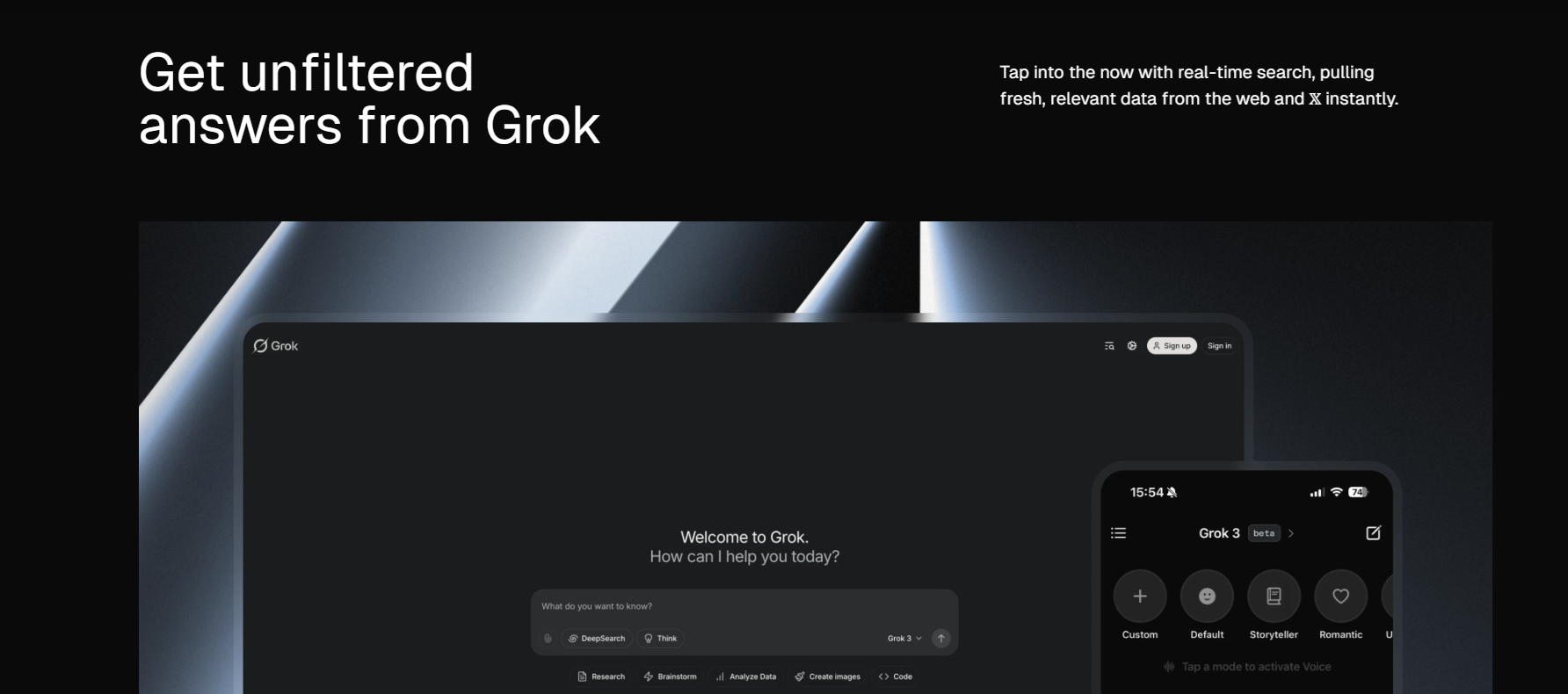
BASEL – Roche, a global leader in pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, has unveiled a groundbreaking automated digital pathology algorithm designed to revolutionize the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Developed to assist pathologists in the identification and measurement of tumor cell staining positivity, the uPath PD-L1 (SP263) image analysis promises faster and more accurate diagnoses, a critical need in the battle against lung cancer.
Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases, making rapid and precise diagnosis imperative for effective treatment strategies. The new algorithm, integrated within Roche’s uPath enterprise software, streamlines the analysis of scanned slide images, providing objective and reproducible assessments to aid in diagnosis and subsequent treatment decisions.
Validated on the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay, the uPath PD-L1 (SP263) algorithm enables pathologists to swiftly determine tumor positivity for the PD-L1 biomarker. This information is vital as patients with PD-L1 positive tumors may be eligible for targeted treatment options.
Thomas Schinecker, CEO of Roche Diagnostics, emphasized the significance of diagnostic consistency and certainty in improving patient outcomes. He stated, “Our uPath PD-L1 (SP263) image analysis for non-small cell lung cancer is the first next-generation CE-IVD PD-L1 algorithm to the clinical market. It expands on our growing digital pathology suite for VENTANA assays that aid physicians in providing the most accurate treatment decisions for patients with the most common type of lung cancer.”
Powered by artificial intelligence, the uPath PD-L1 (SP263) image analysis delivers one-click, whole-slide automated assessments, enhancing efficiency and precision in pathology decision-making. This innovation marks a significant step forward in Roche’s commitment to personalized healthcare and underscores its dedication to advancing digital pathology solutions.
The uPath image analysis algorithm suite offers a comprehensive range of tools for pathology decision support, ensuring rapid and consistent analysis of tissue samples. The launch of the uPath PD-L1 (SP263) image analysis for NSCLC follows the successful introduction of the Roche uPath enterprise software in January 2019.
Roche’s end-to-end digital pathology solution, from tissue staining to clinical image analysis, represents a paradigm shift in diagnostic capabilities. By minimizing variables and standardizing processes, Roche empowers pathologists to make informed clinical decisions with confidence.
The introduction of the uPath PD-L1 (SP263) image analysis for NSCLC algorithm underscores Roche’s commitment to driving innovation in cancer diagnostics and personalized medicine. With lung cancer continuing to pose a significant global health burden, advancements in diagnostic technologies are crucial in improving patient outcomes and reducing mortality rates.