SANTA CLARA — At the Conference for Robot Learning (CoRL) in Munich, Germany, NVIDIA introduced a suite of cutting-edge tools and workflows designed to revolutionize AI-driven robotics. These innovations aim to enhance robot dexterity, control, manipulation, and mobility, ultimately accelerating the development of AI-powered robots, including humanoids.
The announcement featured several key advancements: the public release of the NVIDIA Isaac Lab robot learning framework, six new humanoid robot learning workflows under the Project GR00T initiative, and a range of world-model development tools for video data processing, such as the NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizer and the NeMo Curator for video curation.
NVIDIA’s Cosmos tokenizer, which is now open-source, provides a powerful solution for tokenizing images and video with exceptional speed and compression. Running up to 12 times faster than current alternatives, it allows developers to break down visual data into high-quality tokens at minimal cost. The NeMo Curator significantly improves video processing speeds, delivering curation performance up to seven times faster than unoptimized methods, making it ideal for scaling AI training workflows.

In parallel, NVIDIA unveiled 23 research papers and nine workshops at CoRL, showcasing their leadership in the robot learning field. Notably, the company also announced a collaboration with Hugging Face to boost open-source robotics research, leveraging tools like LeRobot, NVIDIA Isaac Lab, and NVIDIA Jetson to support the developer community.
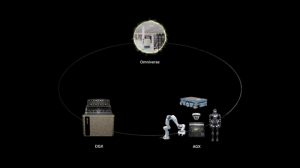
Isaac Lab, built on the Omniverse platform, is designed to simplify robot policy training at scale. This open-source framework applies to various robot types, from humanoids to quadrupeds and collaborative robots, allowing developers to tackle increasingly complex tasks. Leading robotics companies and research institutions worldwide, including Agility Robotics, Boston Dynamics, and Unitree Robotics, are already integrating Isaac Lab into their projects.
Project GR00T, NVIDIA’s ambitious effort to accelerate humanoid robot development, introduces six specialized workflows aimed at addressing the most challenging aspects of building general-purpose humanoid robots. These workflows span areas such as generative AI-powered 3D environments, robot motion, dexterous manipulation, whole-body control, locomotion, and multimodal perception. The initiative’s goal is to provide developers with essential tools and resources to advance humanoid robotics more effectively.
In addition, NVIDIA’s new world-model development tools are designed to streamline the creation of AI models that predict how objects and environments react to robot actions. With the Cosmos tokenizer and NeMo Curator, developers can efficiently manage large-scale image and video data to enhance the accuracy and scalability of world models. These tools also significantly reduce processing time and optimize resource use, making it easier to train advanced AI systems.
At CoRL, NVIDIA also highlighted breakthroughs in robot learning, including new approaches for integrating vision-language models, improving robot navigation, and advancing long-term planning capabilities. The company’s research continues to push the boundaries of humanoid robot control, synthetic data generation, and other essential areas.
Developers can access the latest versions of Isaac Lab and the Cosmos tokenizer immediately via GitHub and Hugging Face, while the NeMo Curator will be available later this month. New workflows from Project GR00T will soon be released, offering even more resources to help developers push the envelope of humanoid robotics.
For further details, including guides, tutorials, and access to NVIDIA’s Humanoid Robot Developer Program, visit the official NVIDIA website.