SANTA CLARA — The humanoid robot market, projected to reach $38 billion in the next two decades, is poised for significant growth, especially in industries like manufacturing and logistics. To meet this growing demand, NVIDIA has unveiled an innovative suite of tools designed to fast-track the development of next-generation humanoid robots. These tools include robot foundation models, synthetic data pipelines, and simulation frameworks, all built to help developers build more capable and efficient humanoid robots.
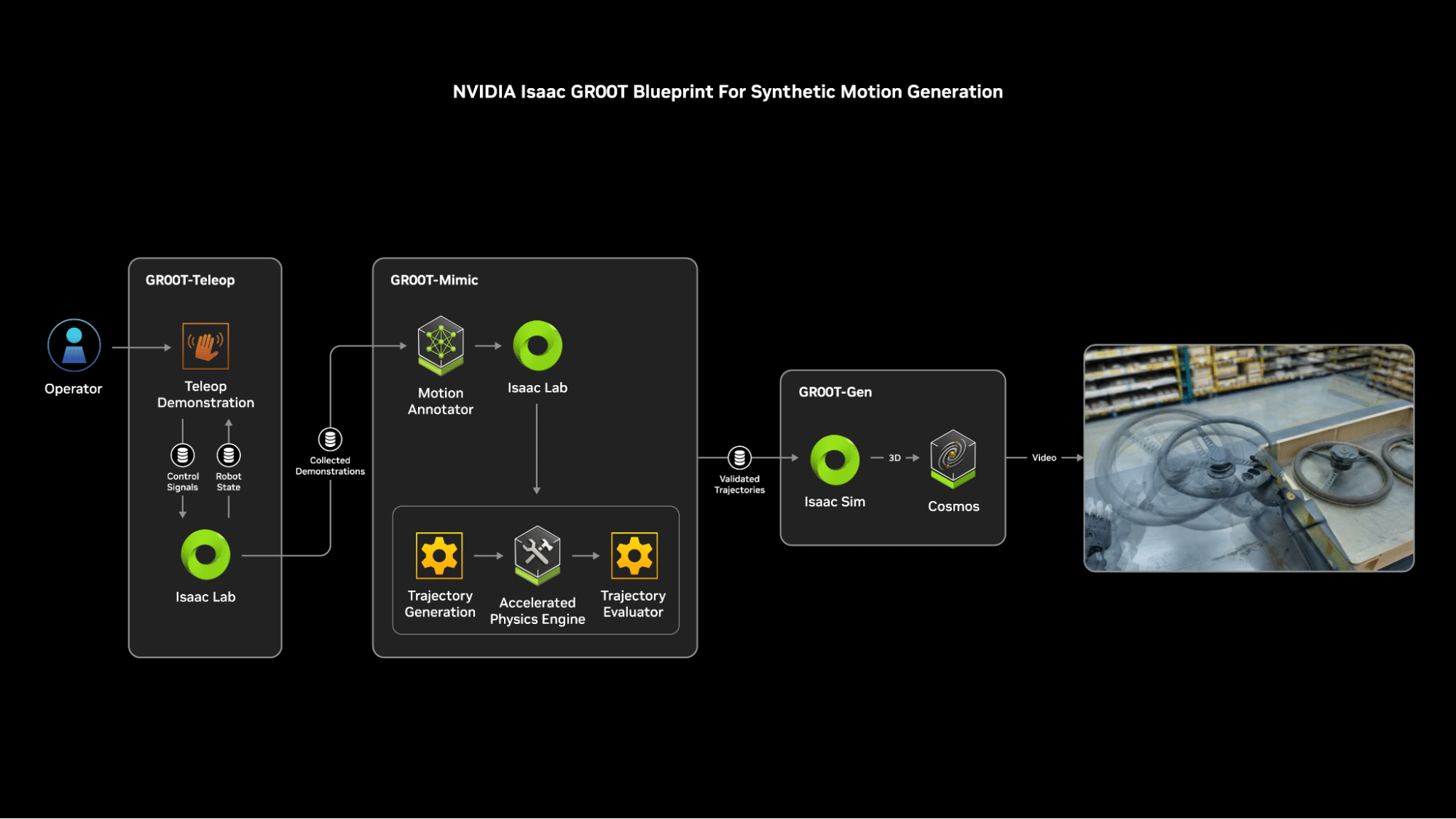
During the CES trade show, NVIDIA’s founder and CEO Jensen Huang announced the release of the Isaac GR00T Blueprint for synthetic motion generation, a major advancement in the world of humanoid robots. This blueprint enables developers to generate massive amounts of synthetic motion data by employing imitation learning, a technique where robots acquire new skills by mimicking human demonstrations.
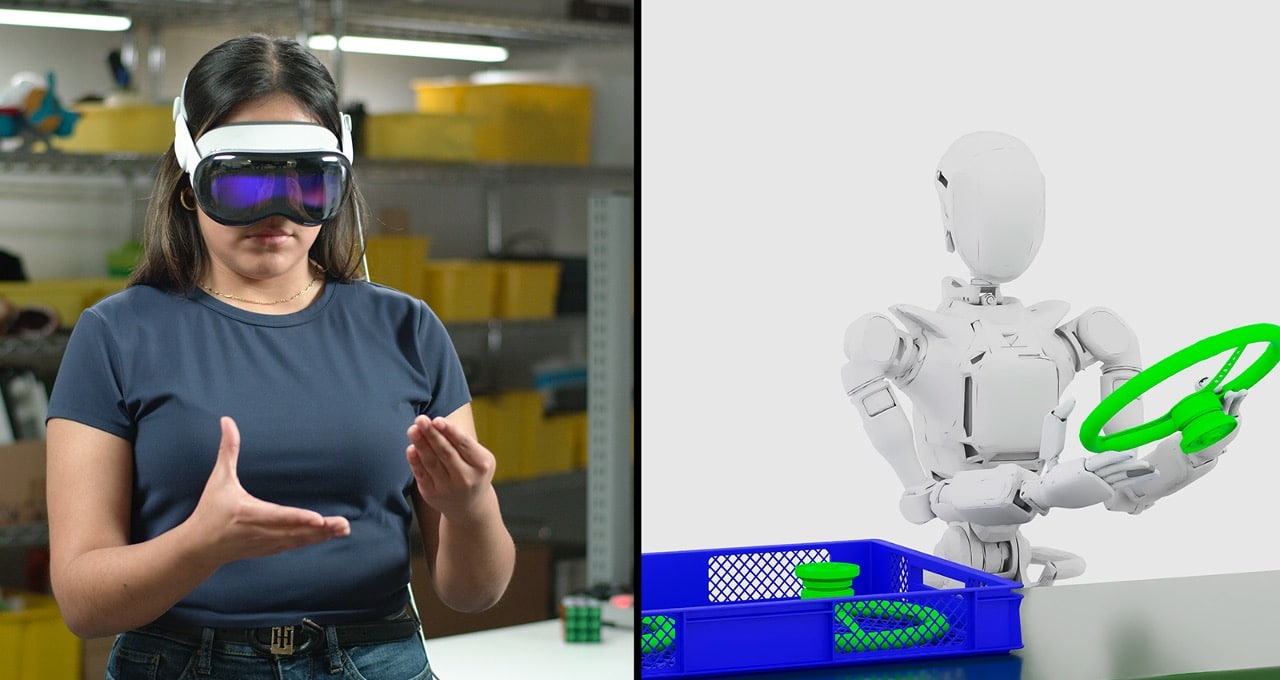
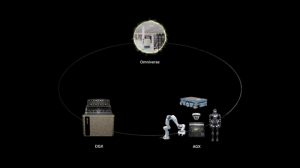
The process begins with the GR00T-Teleop workflow, which uses the Apple Vision Pro to capture human actions in a digital twin, with these actions then being mirrored by a robot in a simulated environment. The next step, the GR00T-Mimic workflow, enhances the captured human demonstrations into a larger synthetic dataset, which is further expanded by the GR00T-Gen workflow. Built on NVIDIA Omniverse and the NVIDIA Cosmos platform, GR00T-Gen uses domain randomization and 3D upscaling to significantly boost the dataset’s size and diversity.
This extensive synthetic data can then be input into the robot’s policy model, allowing it to learn how to interact with and move within its environment. All of this is facilitated within the NVIDIA Isaac Lab, an open-source and modular robot learning framework. The resulting humanoids are equipped with an unprecedented level of motion intelligence and interaction capabilities.
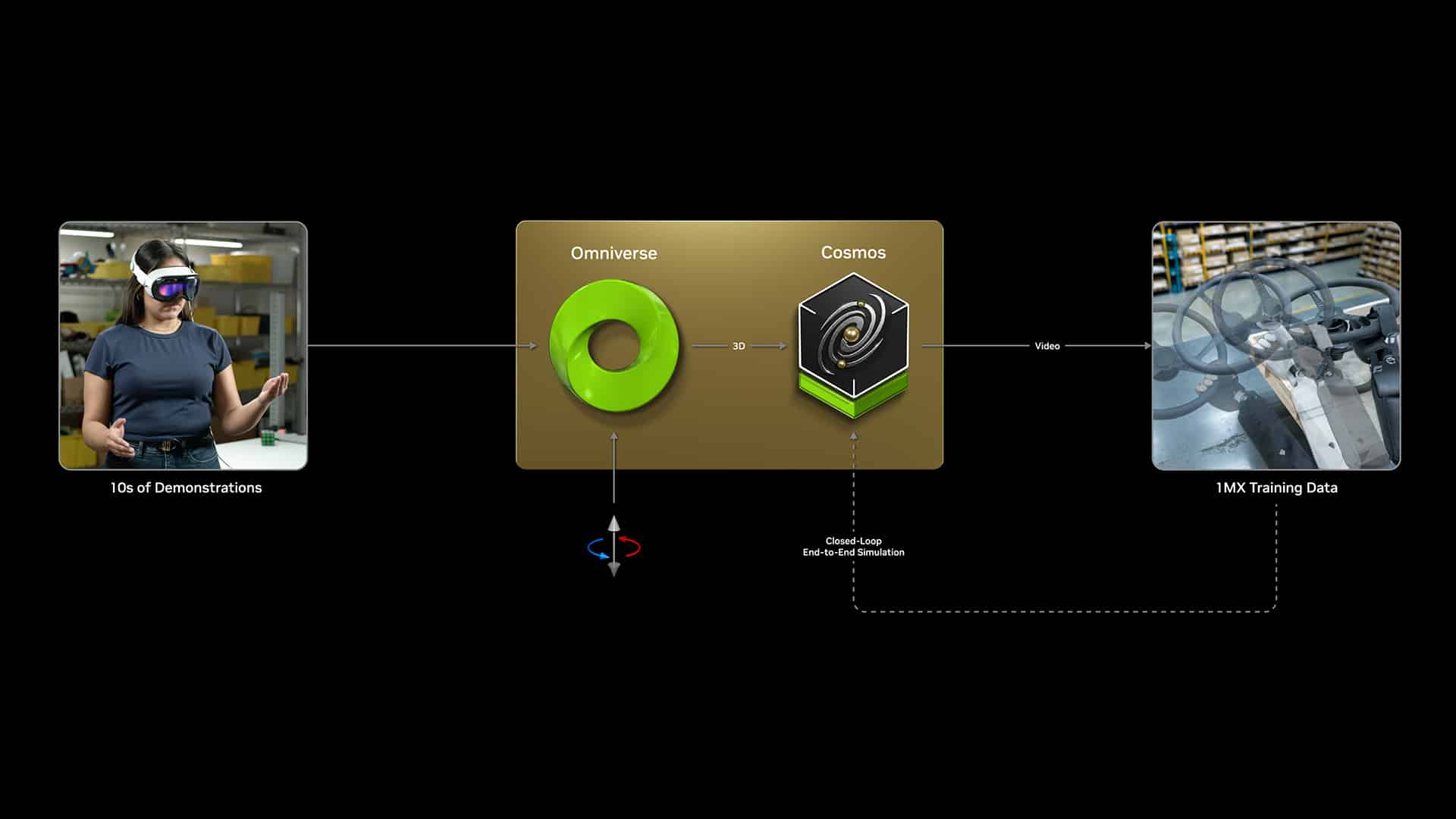
At CES, NVIDIA also introduced Cosmos, a new platform designed to create high-quality, physics-aware videos and world states for physical AI applications. With a family of pretrained autoregressive and diffusion models, Cosmos was trained on an immense 18 quadrillion tokens, including data from autonomous driving, robotics, drone footage, and synthetic data. These models are designed to close the simulation-to-real gap by generating virtual worlds that are incredibly close to real-life physics, minimizing common issues like hallucinations in world models.
Cosmos also integrates seamlessly with Omniverse, NVIDIA’s developer platform for building 3D applications, enabling the creation of more accurate, controllable simulations for humanoid robots. By combining Cosmos and Omniverse, developers can refine their robot models and simulations, ensuring that they work effectively and safely in the real world.
The collaboration between Isaac GR00T, Omniverse, and Cosmos is already gaining traction within the robotics community. Leading companies, including Boston Dynamics and Figure, have begun adopting these technologies and are seeing impressive results in their humanoid robot projects.
Humanoid robot developers are encouraged to apply for early access to NVIDIA’s humanoid robot developer program, which provides resources and support to accelerate the design and development of humanoid robots. To learn more, interested developers can watch Jensen Huang’s CES keynote and follow updates from NVIDIA Robotics on LinkedIn, Instagram, X, and Facebook.
See notice regarding software product information.