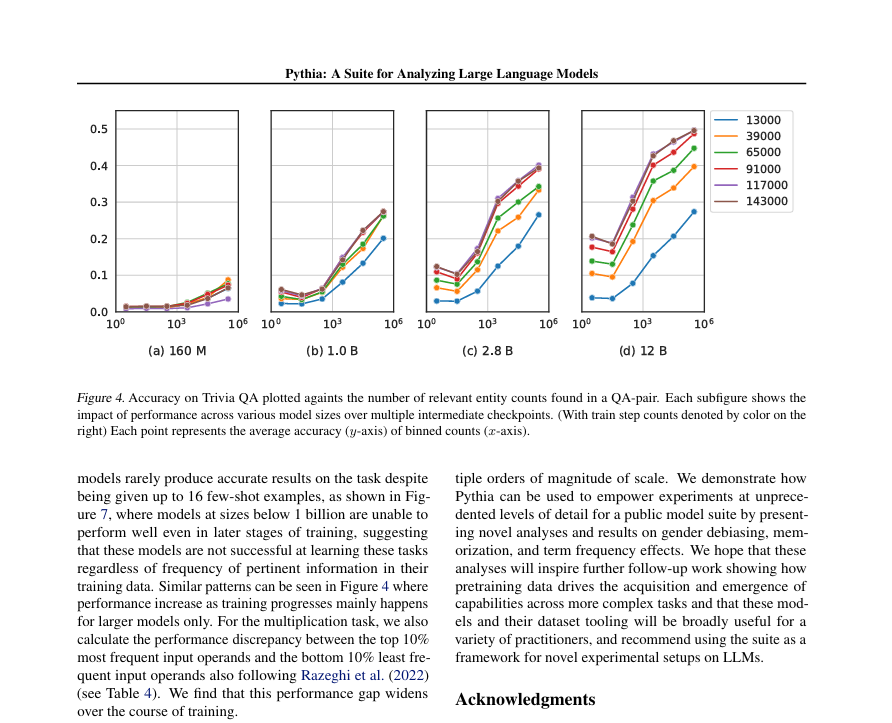
SANTA CLARA — Japan’s healthcare sector is embracing sovereign AI solutions to advance drug discovery, genomics, and medical device development, as healthcare providers and researchers innovate to meet the needs of an aging population. Nearly 30% of Japan’s citizens are over 65, and AI-driven healthcare is seen as vital to addressing an anticipated shortfall of 500,000 healthcare workers by next year.
At the NVIDIA AI Summit Japan, healthcare leaders showcased a range of cutting-edge applications powered by NVIDIA AI computing platforms, including Tokyo-1, a DGX supercomputer, and specialized tools like NVIDIA BioNeMo, MONAI, Parabricks, and Holoscan. These platforms are enabling breakthroughs in fields such as medical imaging, healthcare robotics, and genomic analysis.
In drug discovery, NVIDIA’s BioNeMo platform is empowering Japan’s pharmaceutical sector—one of the world’s largest—with advanced AI tools to analyze biomolecular data. BioNeMo’s new models, such as AlphaFold2 for protein structure prediction and DiffDock for molecular docking, along with BioNeMo Blueprints, offer modular frameworks for enterprise-scale AI in drug development. For example, Astellas Pharma utilizes these models to generate and optimize novel molecular structures, accelerating chemical molecule generation by over 30 times.
Japan’s pharmaceutical companies, including Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Ono Pharmaceutical, are leveraging Tokyo-1’s capabilities for accelerated drug discovery. The supercomputer, developed with Xeureka (a Mitsui & Co. subsidiary), supports complex molecular simulations and confidential computing through NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs, enabling secure collaborative model training.
For genomics, NVIDIA Parabricks aids institutions like the University of Tokyo Human Genome Center in advancing precision medicine by accelerating secondary DNA and RNA data analysis. This government-led genome project focuses on identifying gene variants unique to the Japanese population, paving the way for personalized cancer therapies. Researchers are also utilizing tools like Giraffe within Parabricks to map genomic data to diverse reference genomes.
Japan’s medtech companies are also harnessing AI to enhance radiology and surgical procedures. Fujifilm has developed an AI-driven application that converts CT images into 3D simulations for surgical planning, while Olympus, in collaboration with NTT, has created real-time, cloud-connected endoscopes using NVIDIA Jetson Orin modules. These devices allow efficient processing of medical images, with photonics-based technology from NTT’s IOWN network enabling low latency and high capacity.
The NVIDIA Holoscan platform supports real-time AI robotic systems for radiology and surgery, providing workflows for endoscopy and ultrasound applications. Showa University, for example, uses Holoscan and the NVIDIA IGX platform for surgical microscopy, converting footage into real-time 3D imagery to assist surgeons in locating tumors. Japanese companies like AIM, Anaut, iMed Technologies, and Jmees are exploring Holoscan’s capabilities for diagnostic support in endoscopy and surgery, potentially identifying critical structures or conditions like gastrointestinal cancers during procedures.
Digital health initiatives are equally crucial in Japan’s aging society. Fujifilm’s NURA health screening centers employ AI to streamline cancer and chronic disease diagnostics, using NVIDIA RTX GPUs to generate image-based medical summaries. Fujifilm is also testing NVIDIA MONAI and NeMo for future AI-enhanced healthcare solutions.
For more insights into NVIDIA’s healthcare partnerships in Japan, the NVIDIA AI Summit session by Kimberly Powell, VP of Healthcare, is available on-demand.