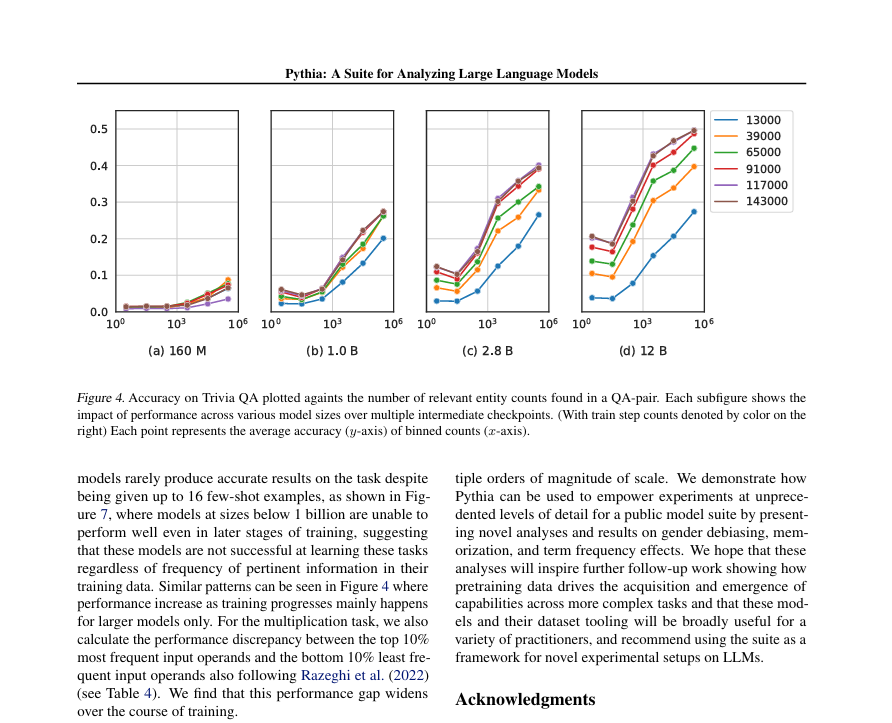
LONDON — Google DeepMind recently announced AlphaProteo, a pioneering AI-driven system designed to generate novel protein binders with applications in biology and health research. Created by DeepMind’s Protein Design and Wet Lab teams, AlphaProteo stands out as the first AI tool capable of designing effective protein binders for targets like VEGF-A, a protein linked to cancer and diabetes-related complications. This breakthrough could propel advancements across multiple research fields, including drug design, diagnostic development, and enhanced understanding of biological processes.
Illustration of a predicted protein binder structure interacting with a target protein. Shown in blue is a predicted protein binder structure generated by AlphaProteo, designed for binding to a target protein. Shown in yellow is the target protein, specifically the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain
AlphaProteo is trained to analyze vast amounts of protein interaction data, including entries from the Protein Data Bank and AlphaFold’s extensive library of predicted structures. Leveraging this knowledge, the AI system can generate candidate proteins that bind with precision to specified target sites, dramatically increasing the potential success rate of experimental protein design. In trials, AlphaProteo outperformed existing methods by producing binders with up to 300 times stronger binding affinity across seven tested targets, which include SARS-CoV-2 and cancer-related proteins like IL-7Rɑ and PD-L1.
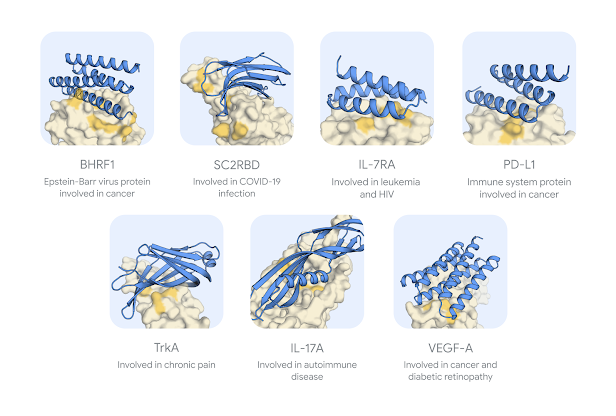
The technology was further validated by independent researchers from the Francis Crick Institute, who confirmed AlphaProteo’s accuracy and biological efficacy in tests involving key protein interactions. Notably, some AlphaProteo-generated binders were able to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 from infecting cells, underscoring the system’s potential for disease mitigation and other critical applications.
AlphaProteo represents an advancement in overcoming the time-consuming challenges of traditional protein design, with fewer experimental rounds needed to achieve effective binding. It demonstrates competitive success rates across complex targets, although certain challenging proteins like TNFɑ remain outside its current design capacity. Google DeepMind acknowledges the importance of ongoing improvements to AlphaProteo, aiming to enhance its scope and reliability to address increasingly intricate bioengineering problems.
To ensure responsible use of AlphaProteo’s capabilities, Google DeepMind collaborates with biosecurity experts and is contributing to frameworks for safe AI deployment in biological research. With continued refinement, AlphaProteo holds promise for a wide range of scientific advancements, from developing new therapeutic solutions to supporting sustainable manufacturing processes.