Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA) has evolved into one of the most influential technology powerhouses of our time. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang alongside Chris Malachowsky and Curtis Priem and originally celebrated for its groundbreaking graphics processing units (GPUs), the company has continually reinvented itself—expanding its expertise well beyond gaming into areas such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, high-performance computing, and autonomous vehicles.
Their GPUs are used in a wide range of applications, from video games to cryptocurrency mining to machine learning. They’ve been a key player in the AI revolution because their GPUs are well-suited for the parallel processing required by many AI algorithms.
According to the Nvidia About page, the company’s mission centers on transforming computing by pushing the limits of what’s possible with visual and AI technologies. This commitment to innovation is further detailed in the Nvidia Story PDF, which outlines a journey from pioneering high-quality graphics to creating comprehensive computing platforms that power industries ranging from entertainment to scientific research.
As noted by Wikipedia, Nvidia’s robust legacy in visual computing has made its GPUs a cornerstone in modern gaming and professional visualization. Today, the company leverages this heritage to lead in emerging fields. Their groundbreaking work in AI and deep learning, detailed on the Nvidia Research portal, continues to redefine what’s possible—from enhancing virtual reality experiences to accelerating the discovery processes in scientific research.
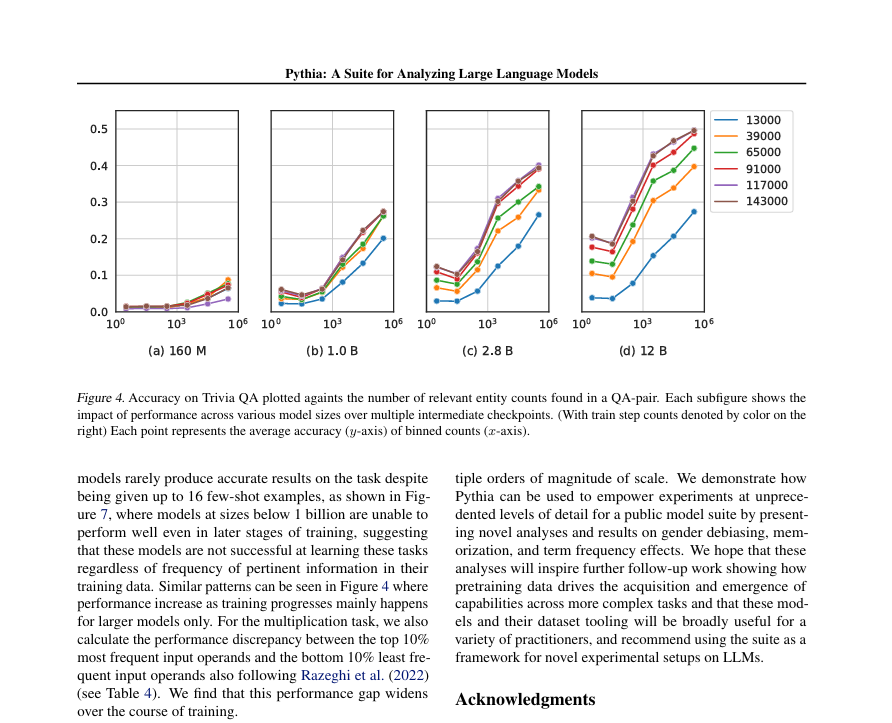
Nvidia is clearly making significant inroads into the healthcare and medical research sectors, leveraging their AI and GPU technologies.
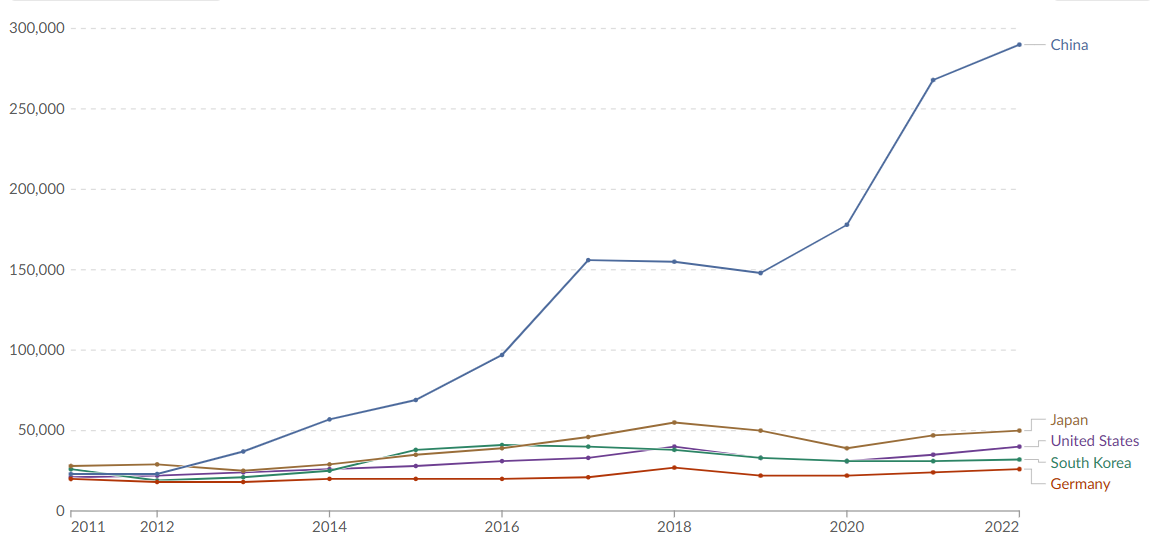
The company’s financial health and strategic growth are evident on the Nvidia Investor page and financial platforms like Yahoo Finance and Google Finance, which reflect a solid market performance and a clear commitment to reinvesting in future technologies. Nvidia’s innovative spirit is also mirrored in its involvement with the startup ecosystem, as highlighted by its profile on Crunchbase. Over the past decade, Nvidia has experienced unprecedented growth, with annual revenue soaring from approximately US$4.7 billion in 2014 to nearly US$61 billion in 2023, and net income surging from US$631 million to almost US$30 billion in the same period. Additionally, its market capitalization rocketed from over US$328.7 billion in January 2021 to around US$2.98 trillion by late Q3 2024, while as of Feb 2025 its market capitalization has further soared to an astonishing US$3.40 trillion, underscoring its transformation into a global technology powerhouse.
Here is a quick overview of the Company’s phenomenal growth trajectory over the past decade:
- Revenue Expansion: From roughly US$4.7 billion in 2014 to nearly US$61 billion in 2023, Nvidia’s revenue has grown more than 13 times, reflecting both market expansion and strategic diversification.
- Profitability Surge: Net income grew from US$631 million in 2014 to almost US$30 billion in 2023, highlighting significant improvements in operating efficiency and margin expansion.
- Workforce and Scale: The employee count increased from 6,384 in 2014 to nearly 29,600 in 2023, mirroring the company’s broadening scope and operational complexity.
- Market Impact: The evolution in market capitalization—from US$328.7 billion in early 2021 to US$3.40 trillion in Q2 2025—underscores Nvidia’s status as a dominant force in the semiconductor and technology sectors, as well as its transformative impact on industries like AI, high-performance computing, and gaming.
Beyond technology and market performance, Nvidia places a strong emphasis on community engagement and social responsibility. The Nvidia Foundation and the company’s CSR initiatives underscore a dedication to empowering communities, supporting education, and promoting sustainable practices. This blend of innovation and corporate responsibility not only enhances their brand reputation but also demonstrates a commitment to making a positive impact in society.
Nvidia’s expansive suite of technologies—documented on the Nvidia Technologies page—covers a wide array of applications from gaming and professional visualization to data centers and automotive technology. The company’s dynamic online presence, including platforms such as YouTube, LinkedIn, X (Twitter), and even communities like Reddit’s r/nvidia, highlights its commitment to transparency and open dialogue with its global audience. As stated on these channels, Nvidia not only shares its innovations but also actively engages with enthusiasts, developers, and investors worldwide.
Nvidia stands out as a beacon of technological advancement. Its evolution from a graphics company to a leader in AI and high-performance computing illustrates a visionary approach to technology that continues to shape industries and improve everyday experiences. With a strong commitment to research, a clear focus on sustainability, and active community engagement, Nvidia remains at the forefront of transforming our digital world.
What’s the radical shift here?
The radical shift for Nvidia lies in its transformation from a company primarily known for its gaming graphics processing units (GPUs) into a comprehensive leader in artificial intelligence and high-performance computing. Originally celebrated for revolutionizing visual computing for entertainment and professional graphics (as highlighted on Wikipedia), Nvidia has expanded its focus to include deep learning, autonomous vehicles, data centers, and scientific research. This strategic pivot has repositioned Nvidia as a driving force behind modern computing innovations, influencing not just gaming but virtually every industry that relies on advanced computation and AI.
And what’s the Nvidia’s impact on the AI industry?
Nvidia’s GPUs and related technologies have been a cornerstone for the AI revolution. By providing the computational power needed for training and running complex neural networks, they’ve accelerated breakthroughs in deep learning, computer vision, and autonomous systems, fundamentally reshaping the AI industry.