MENLO PARK — Meta has unveiled the Purple Llama initiative, a comprehensive project designed to provide open-source tools and safety evaluations aimed at helping developers deploy generative AI models responsibly. Authored by Meta, this new effort emphasizes trust and safety, aligning with the best practices outlined in their Responsible Use Guide. As part of the initial rollout, Meta is introducing two key components: CyberSec Eval, a set of cybersecurity safety evaluation benchmarks for large language models (LLMs), and Llama Guard, a safety classifier that facilitates input/output filtering for ease of deployment.
In collaboration with industry giants like AI Alliance, AMD, AWS, Google Cloud, Hugging Face, IBM, Intel, and others, Meta is working to integrate these tools into the broader AI development landscape. These partnerships aim to further the availability of these resources to the open-source community, ensuring a more secure and ethically responsible AI ecosystem.
Generative AI is reshaping innovation, with Llama models playing a significant role in fueling advancements, especially given the over 100 million downloads to date. However, as AI capabilities evolve, so do the challenges associated with ensuring its responsible use. By launching Purple Llama, Meta aims to centralize tools and frameworks that will allow developers to build AI systems with a stronger focus on trust and safety.
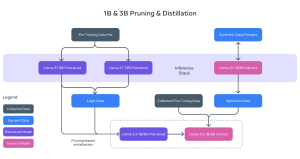
The first step in this project is the release of cybersecurity evaluations and safeguards for AI-generated content. CyberSec Eval offers the first industry-wide benchmarks that assess the cybersecurity risks associated with LLMs, drawing on industry standards such as CWE and MITRE ATT&CK. These tools evaluate potential risks, such as insecure code generation and assistance in cyberattacks, offering a proactive approach to mitigating security threats in AI development. Meta’s CyberSec Eval paper delves deeper into these findings.
Additionally, the launch of Llama Guard provides an openly accessible model for content filtering, trained on publicly available datasets to detect and prevent potentially harmful outputs. This model offers developers a valuable resource for ensuring their AI systems adhere to responsible content guidelines, further discussed in the Llama Guard paper. Meta’s open approach enables customization, empowering the developer community to adapt the model to their specific use cases.

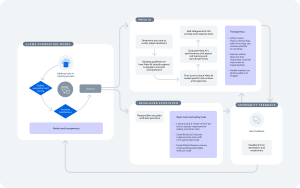
Meta’s commitment to fostering an open ecosystem is reflected in the collaborative nature of the Purple Llama project, which embraces both offensive (red team) and defensive (blue team) postures. This “purple teaming” approach underscores Meta’s comprehensive strategy for addressing the multifaceted risks posed by generative AI.
With a solid track record in open science, Meta continues to champion collaborative research and open-source initiatives. The company remains committed to engaging with industry partners and AI developers to refine and enhance trust and safety tools. This collaborative effort will be further highlighted at the upcoming NeurIPS 2023 workshop, where Meta will present technical deep dives into these tools.
Through the Purple Llama project, Meta is reinforcing its vision of a responsible, open AI ecosystem where trust and safety are paramount to the future of generative AI.